The Core Principle: Mechanical Shearing
At its most fundamental level, a plastic crusher operates on the principle of mechanical shearing. It uses the powerful, scissor-like action between moving and stationary blades to cut,
tear, and shred plastic materials into smaller particles.
Step-by-Step Working Principle
The process can be broken down into the following stages:
1. Power Transmission and Initiation:
An electric motor provides the initial power.
This power is transferred to the crusher's main shaft via a belt and pulley system. This system allows for high-speed rotation and provides the necessary torque for crushing.
2. Formation of the Shearing Zone:
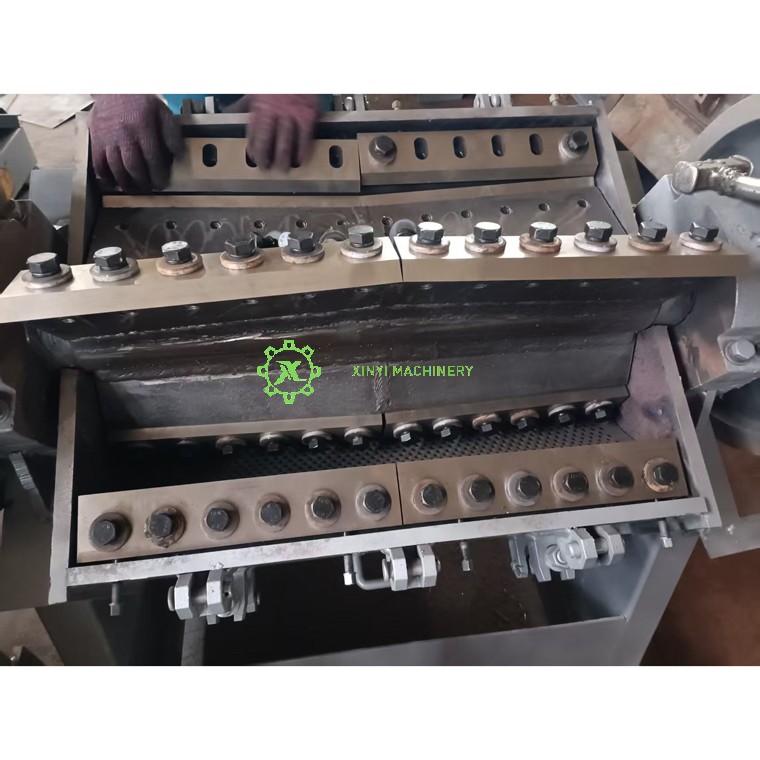
The rotating main shaft, called the rotor, has multiple rotor blades attached to it.
Directly opposite the path of these rotating blades are stationary bed knives (or stator blades), fixed to the crusher's main body.
As the rotor spins at high speed, the small gap between each passing rotor blade and the fixed bed knife creates a shearing port or cutting point.
3. Feeding and Primary Size Reduction:
Plastic material is fed into the crushing chamber through a hopper.
It is immediately engaged by the rotating rotor blades.
The continuous opening and closing of the shearing port slices and shears the plastic into smaller pieces through a powerful scissoring action.
4. Screening and Classification:
The crushed plastic falls downward within the chamber.
A screen or sieve (with a specific mesh size) is mounted at the bottom of the crushing chamber.
Particles that are smaller than the screen's openings fall through immediately and are discharged, ready for reprocessing.
5. Recirculation and Final Reduction:
Larger particles that cannot pass through the screen are retained in the crushing chamber.
The internal airflow (a vortex) created by the high-speed rotation of the rotor lifts these larger pieces and carries them back up into the path of the rotating blades for further cutting.
This recirculation process continues iteratively until all material is small enough to pass through the screen, ensuring a consistent granule size.
Key Maintenance Focus: Bearings and Lubrication
As correctly noted in the source text, the shaft side bearings are critical. They support the heavy rotor and endure significant stress.
Lubrication: Regular lubrication is essential to reduce friction and dissipate heat.
Grease: A high-temperature, high-load lithium-based grease is standard. (The term "butter" is a common industrial slang for grease).
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) Grease: This is an excellent recommendation for heavy-duty applications. Molybdenum disulfide acts as an extreme pressure (EP) additive, providing
superior protection under the high-shock loads encountered during crushing.
Summary
In summary, the plastic crusher's operation is a continuous cycle of:
Shearing plastic between rotating and fixed blades.
Screening the output to separate correctly sized particles.
Recirculating oversized particles for further reduction.
This efficient mechanical process is why crushers are indispensable for rapid size reduction and recycling in the plastics industry. Proper maintenance, especially of the bearings and
blades, is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.