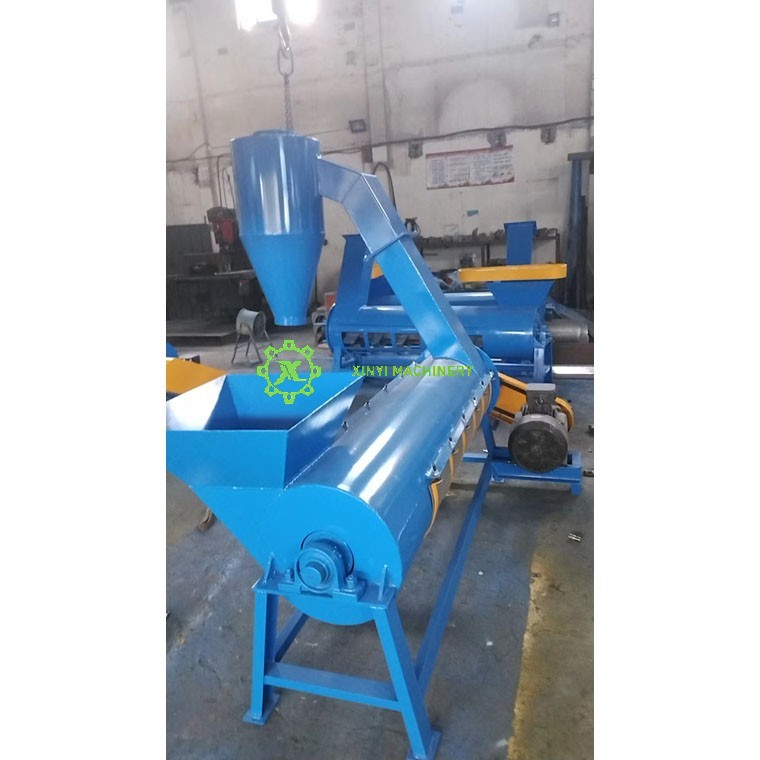
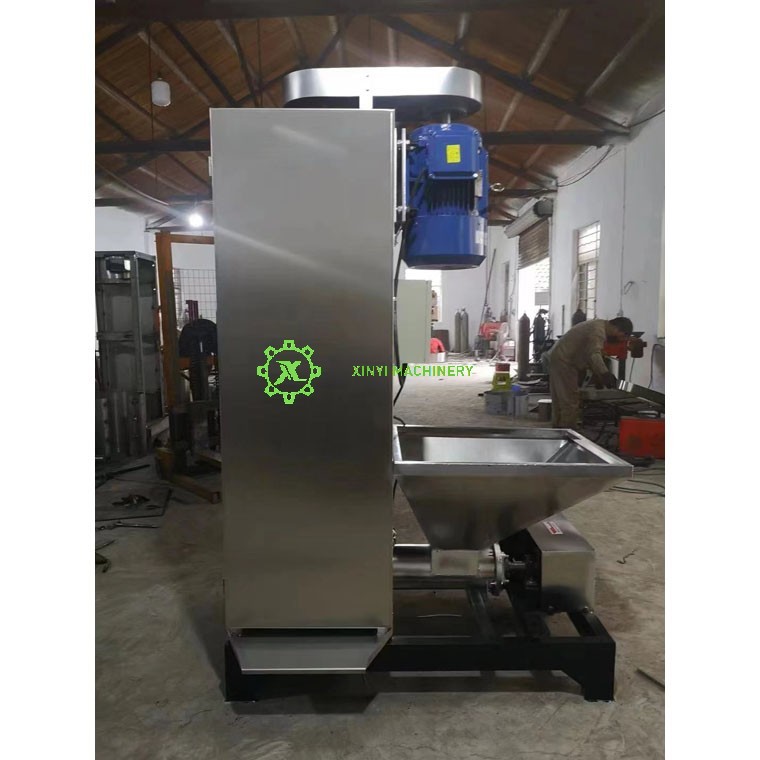
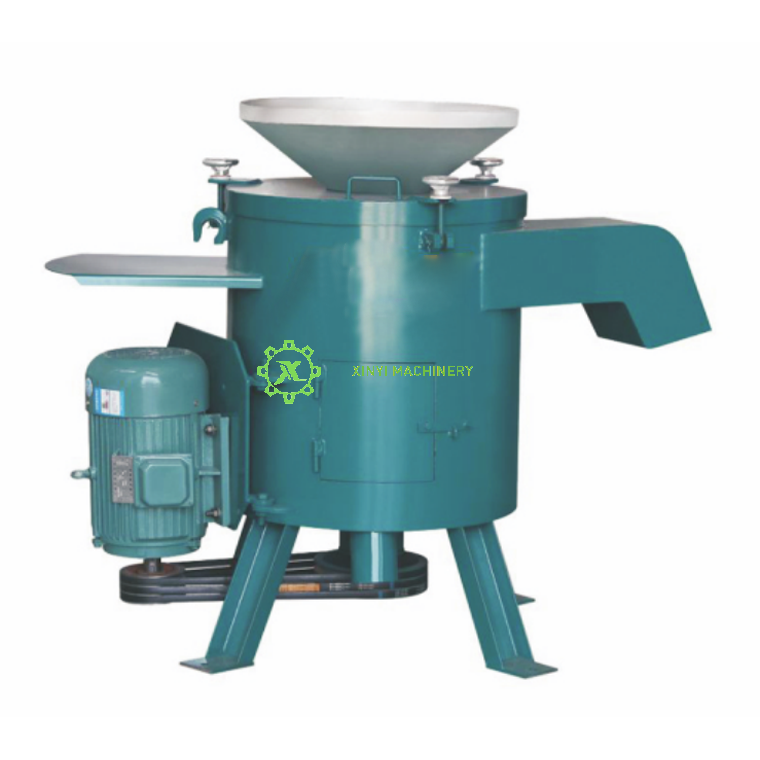
A Plastic Dewatering Machine (also known as a centrifugal dryer, spin dryer, or dewaterer) is a mechanical device used primarily in plastic recycling and processing to remove surface water from plastic flakes, pellets, or regrind after washing and before final thermal drying.
Here's a breakdown of its function, working principle, and importance:
Purpose:
To efficiently separate free water (water clinging to the surface of plastic pieces) from the plastic material.
It is not designed to remove internal moisture bound within the plastic itself – that requires a thermal dryer.
Its main goal is to significantly reduce the moisture content before the material enters a thermal dryer, making the final drying stage much faster, more energy-efficient, and cost-effective.
Working Principle (Centrifugal Force):
Water: Drains out of the machine and is usually collected or sent for treatment/reuse.
Plastic: Once dewatered, the plastic is discharged from the basket, typically via a chute or conveyor, ready for the next stage (often thermal drying).
Feeding: Wet plastic flakes/pellets are fed into a rotating basket (drum) lined with a perforated screen.
Spinning: The basket spins at high speed (typically 800-1500 RPM).
Centrifugal Force: This rapid rotation generates strong centrifugal force. The force flings the heavier plastic pieces outward against the screen wall.
Water Separation: The lighter water is forced through the screen's perforations, separating it from the plastic.
Discharge:
Key Components:
Rotating Basket/Drum: The core component with a perforated screen wall.
Motor: Drives the basket rotation.
Housing/Base: Encloses the mechanism, collects water, and provides structural support.
Feed Hopper: Where wet material enters.
Discharge Chute/Outlet: Where dewatered plastic exits.
Water Drain Outlet: Where separated water drains out.
Vibration Dampers: Reduce machine vibration during operation.
Control Panel: For start/stop and sometimes speed control.
Where it's Used:
Plastic Recycling Plants: Essential after flake wash lines (especially for PET, HDPE, PP, PVC bottles, containers, etc.) before thermal drying.
Plastic Manufacturing: To dewater regrind or pellets that may have gotten wet during processing or storage.
Post-Consumer & Post-Industrial Plastic Processing.
Benefits:
Energy Savings: Removes ~80-95% of surface water mechanically, drastically reducing the energy needed by downstream thermal dryers.
Increased Throughput: Thermal dryers work much faster on pre-dewatered material.
Reduced Drying Time: Shortens the overall drying cycle.
Compact & Efficient: Does a large amount of water removal in a relatively small footprint.
Lower Operating Costs: Significant reduction in thermal energy (gas/electricity) costs.
Improved Final Product Quality: Consistent moisture levels entering the thermal dryer lead to better final product quality.
Limitations:
Surface Water Only: Does not remove internal moisture (requires heat).
Residual Moisture: Leaves material damp (typically 3-8% moisture depending on plastic type and flake size), requiring further drying for most processing.
Material Suitability: Works best on rigid plastic flakes and pellets. Fine powders or films may not separate effectively or could damage the screen.
Screen Maintenance: Screens can wear or get clogged and need periodic inspection/cleaning/replacement.
In simple terms: Think of it like a giant, industrial-strength salad spinner for plastic flakes. It spins the wet plastic incredibly fast, forcing the water out through holes, leaving the plastic significantly drier but still slightly damp, ready for the final heat-drying step. It's a crucial piece of equipment for making plastic recycling and processing more efficient and economical.